超声波换能器 Ultrasonic Transducers
cMUT and pMUT
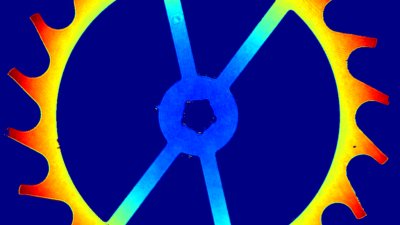
MUTs transform an electrical signal into an acoustic one, through a mechanical complex movement. Designers make use of several electrical, mechanical and acoustical models, and each of them depends on many physical parameters. Therefore, there is a strong need to compare simulation and in-situ experimental results.
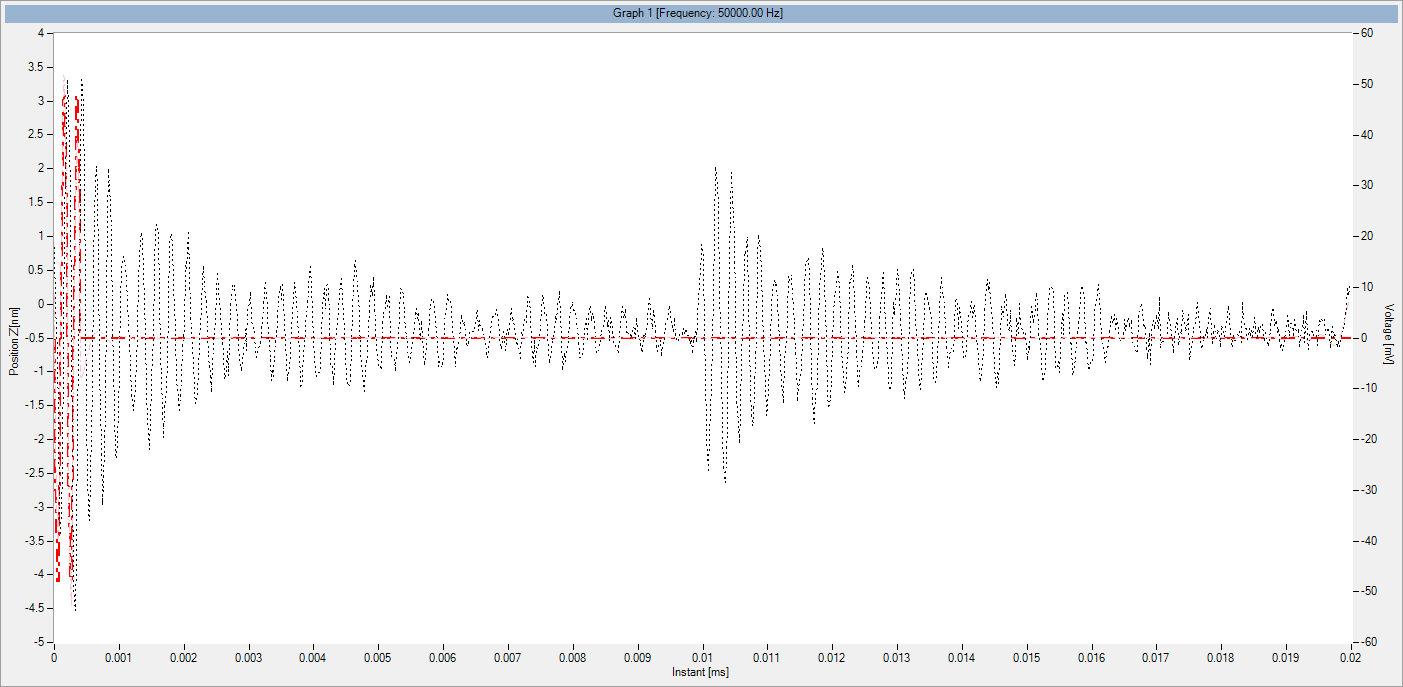
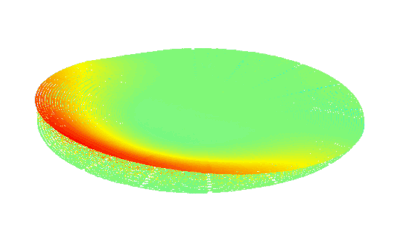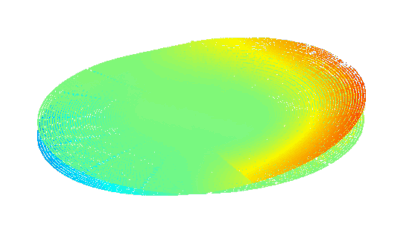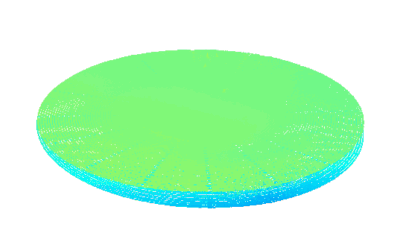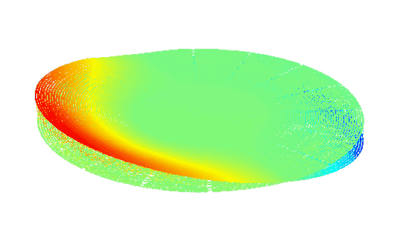
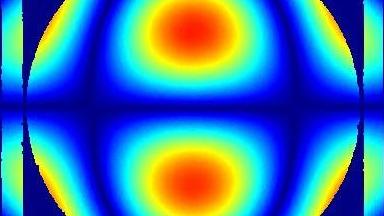
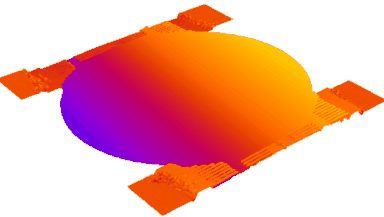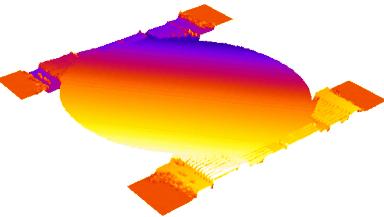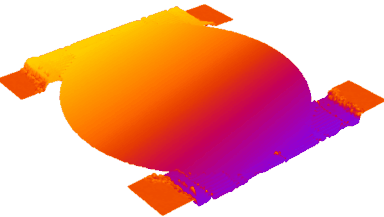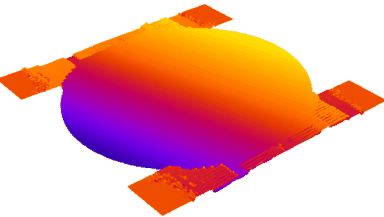
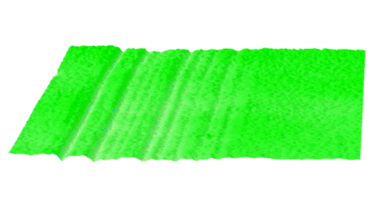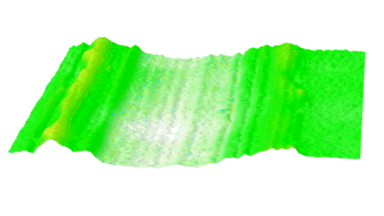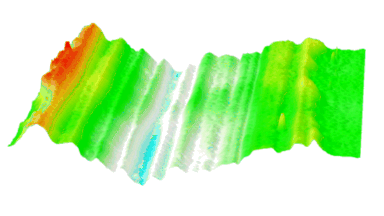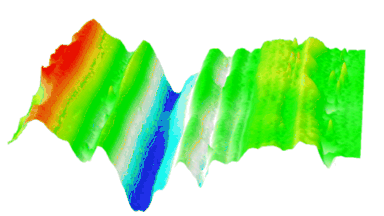
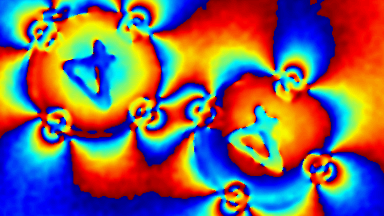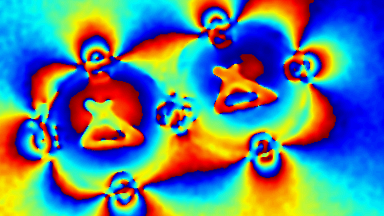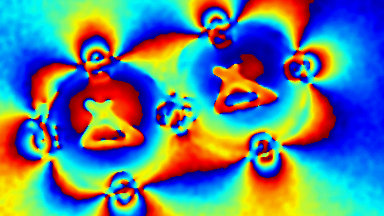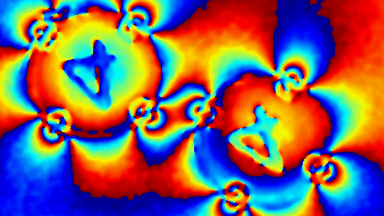
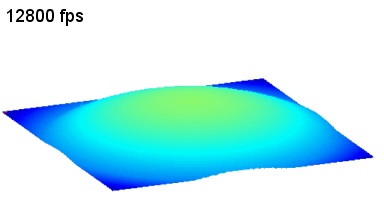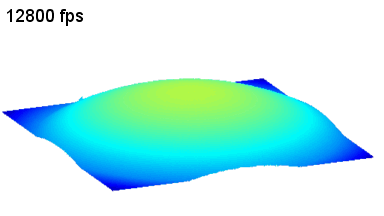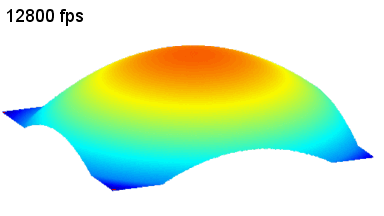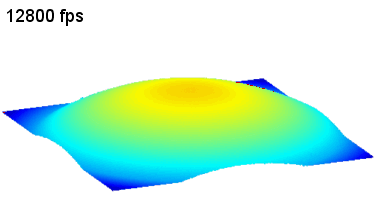
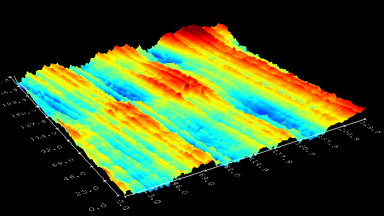
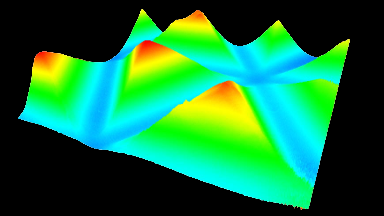
The main vector for this signal transfer is the membrane movement of the MUT. Measurement of its 3D topography time-sequence along the phase of the excitation signal is needed for understanding the energy transfer processes.
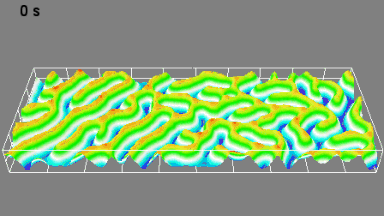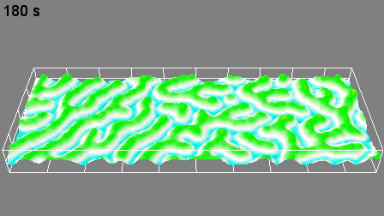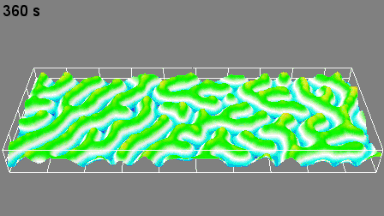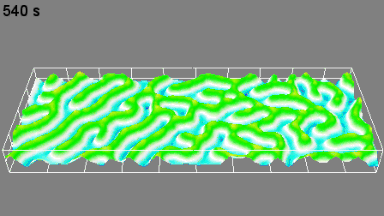
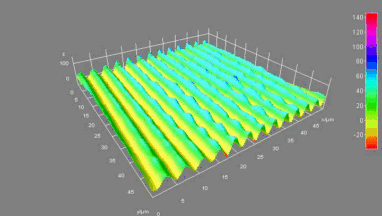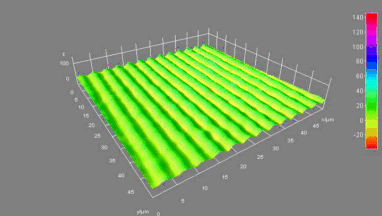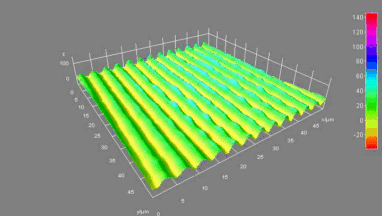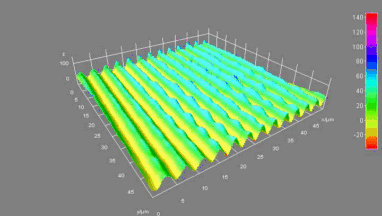
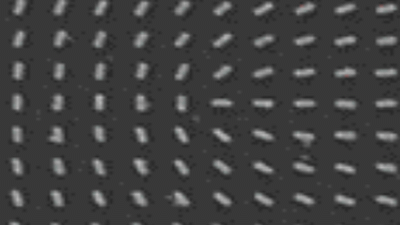
Cross talks and surface waves
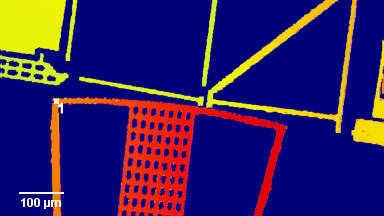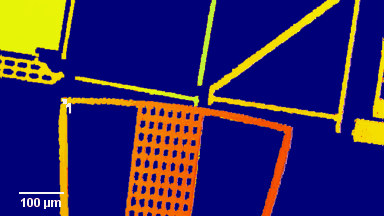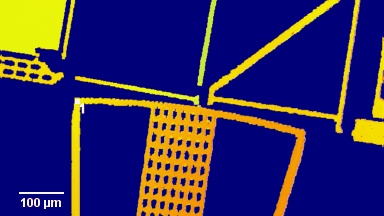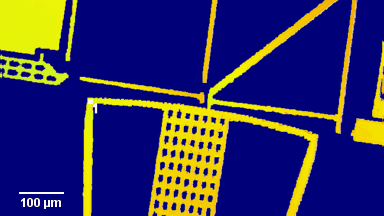
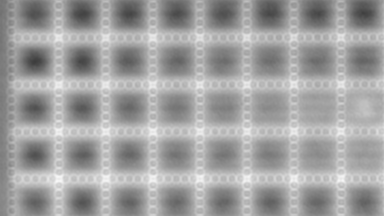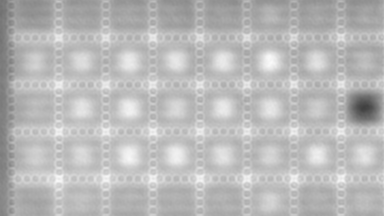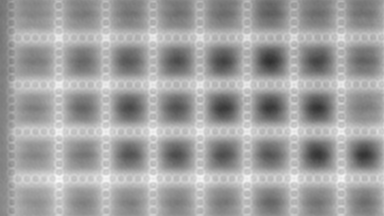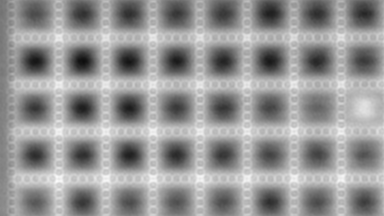
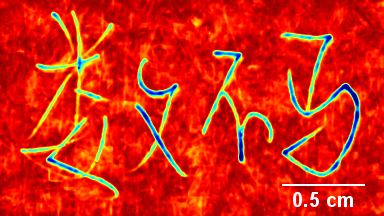
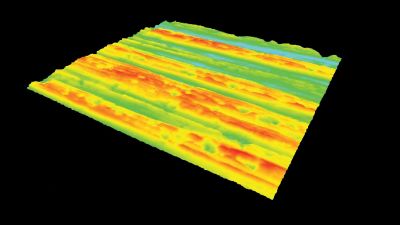
Full field measurement enables simultaneous characterization of many MUT membranes. It enables analysis of:
- cross talk between neighboring membranes
- surface wave propagation
- statistical distribution of membranes characteristics
- the quality of the device
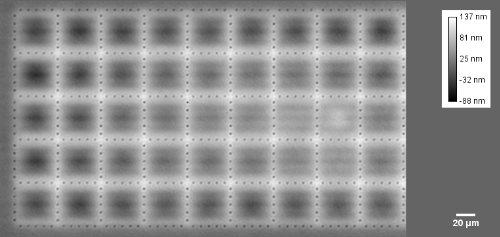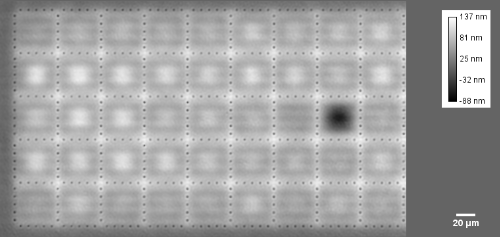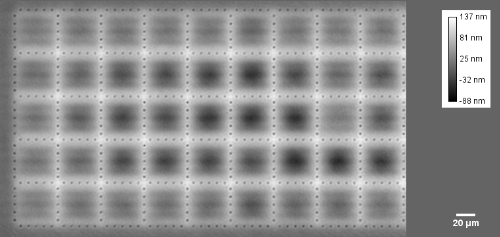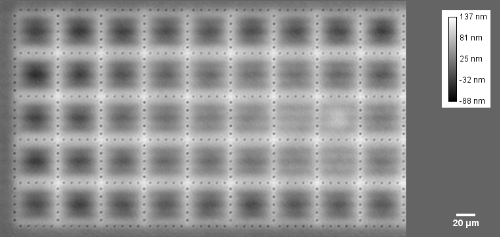
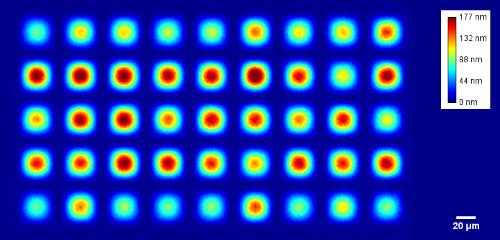
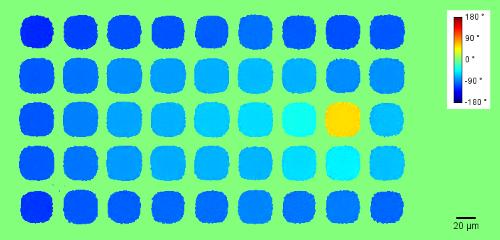
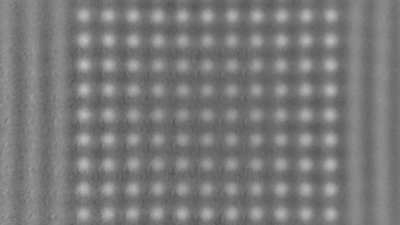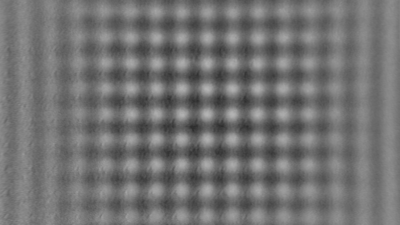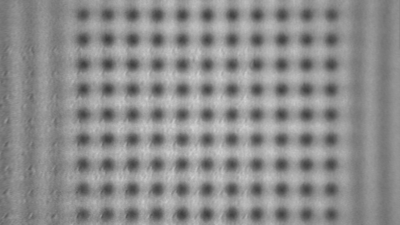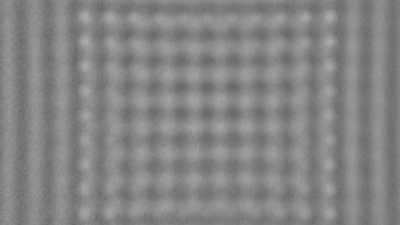
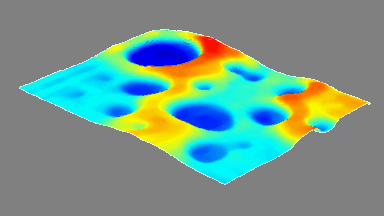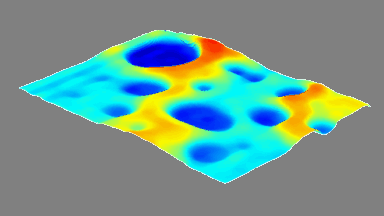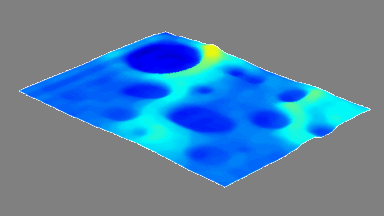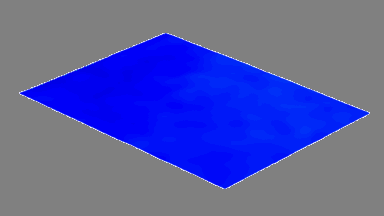
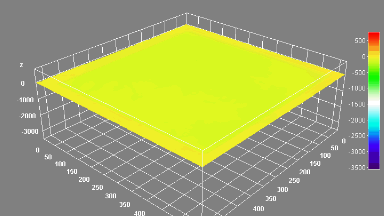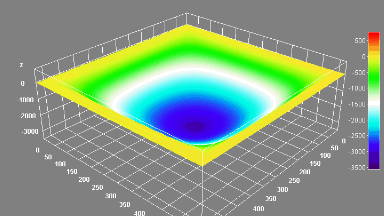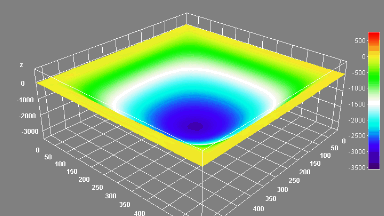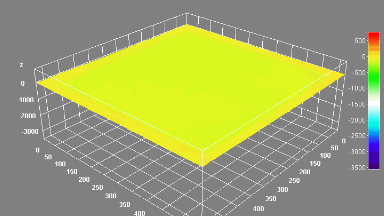
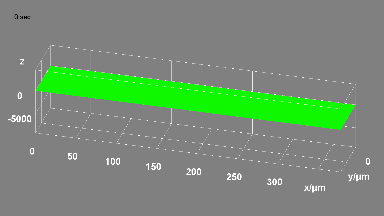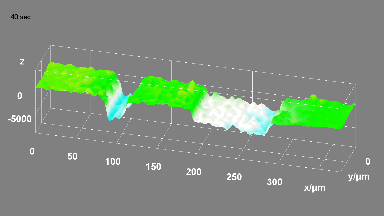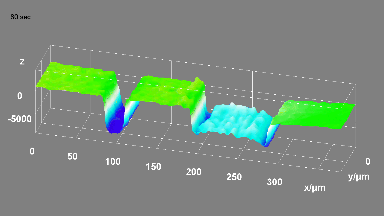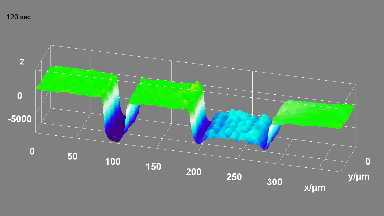
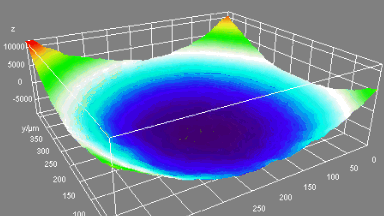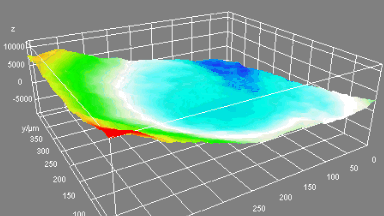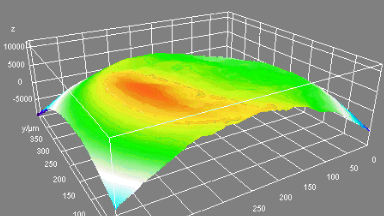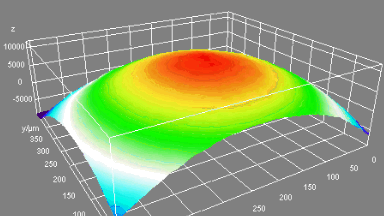
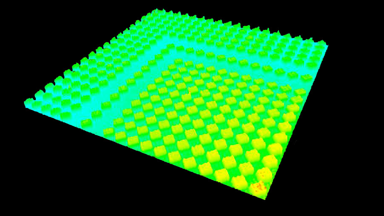
Membrane topography – collapse voltages
The topography of each membrane is measured over its complete surface with high lateral resolution, enabling:
- measurement of the 3D temporal evolution of any membrane point along its excitation cycle with high temporal resolution
- determination of collapse voltage
Characterization of cMUT by Dynamic Holography Microscopy – IEEE Conference Publication
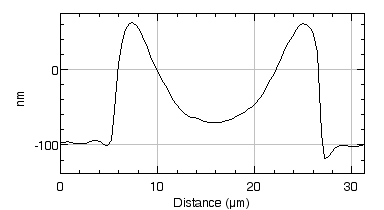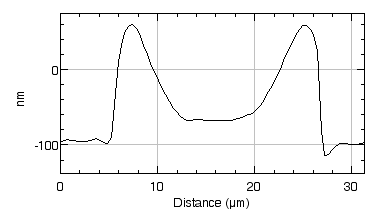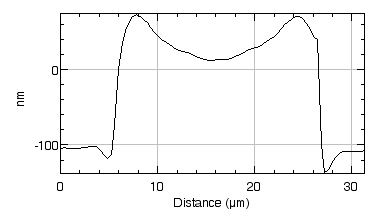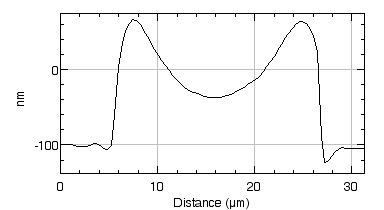
Measure in burst mode
Lyncée Tec stroboscopic module enables short burst mode excitation, commonly used for medical imaging modes.
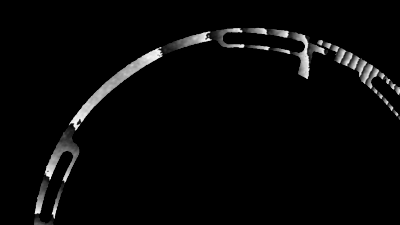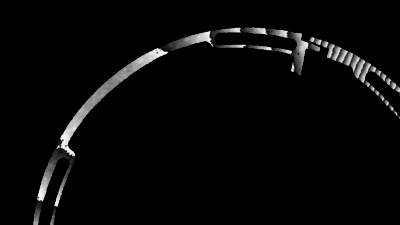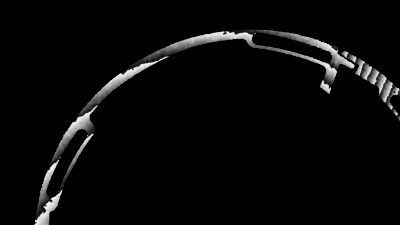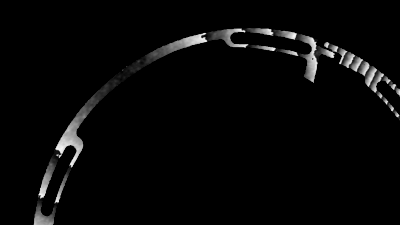
Record echo in immersion
The DHM® unique optical configuration enables measurement of the deformation of immersed membranes resulting from both the transmitted wave and the receiving acoustic echo.